Urgent Care vs Emergency Care sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Understanding the distinctions between urgent care and emergency care is crucial for making informed decisions about medical needs. Let’s delve into the key variances and scenarios that dictate when each type of care is appropriate.
Urgent Care vs Emergency Care

When it comes to seeking medical attention, understanding the differences between urgent care and emergency care is crucial for making the right decision based on the situation at hand.
Key Differences
- Urgent care centers are best for non-life-threatening injuries or illnesses that require immediate attention but are not severe or critical.
- Emergency rooms are equipped to handle life-threatening conditions and medical emergencies that require immediate and intensive care.
- Urgent care centers typically have shorter wait times and lower costs compared to emergency rooms.
Examples of When to Go
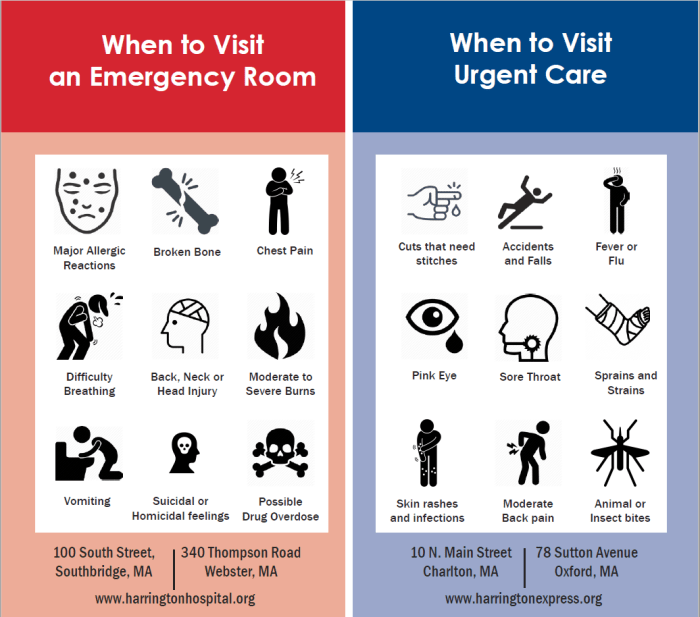
- Urgent Care: Minor injuries like sprains, minor cuts, fever, or minor infections.
- Emergency Care: Chest pain, difficulty breathing, severe burns, head injuries, or major trauma.
Services Offered
- Urgent Care Centers: Treatment for minor injuries and illnesses, X-rays, lab tests, prescription refills, and vaccinations.
- Emergency Rooms: Advanced diagnostic tests, surgery, intensive care, treatment for severe trauma, and critical care.
EMERGENCY CARE

In the realm of healthcare, emergency care refers to the immediate treatment of medical conditions that pose a serious threat to a person’s health or life. These situations require prompt attention to prevent further complications or even death.
Qualifying Medical Emergencies
- Heart attack: Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
- Stroke: Signs include sudden numbness or weakness, confusion, and trouble speaking.
- Severe trauma: Such as a serious injury from a car accident or a fall.
- Severe burns: Extensive burns that cover a large area of the body.
Emergency Room Procedures
Upon arrival at an emergency room, patients are typically triaged based on the severity of their condition. Those with life-threatening issues are prioritized for immediate care. Once stabilized, patients may undergo diagnostic tests such as X-rays, blood work, or CT scans to identify the cause of their symptoms. Treatment may involve medications, surgical intervention, or other forms of therapy depending on the diagnosis.
In conclusion, being aware of the differences between urgent care and emergency care can help individuals navigate healthcare options effectively. By recognizing the unique services and situations that each type of care caters to, individuals can ensure they receive the most suitable and timely medical attention when needed.
Helpful Answers
When should I choose urgent care over emergency care?
Urgent care is ideal for non-life-threatening conditions that require prompt attention but do not warrant a visit to the emergency room, such as minor injuries, fevers, or infections.
What constitutes a medical emergency that necessitates going to the emergency room?
A medical emergency typically involves severe symptoms like chest pain, difficulty breathing, sudden numbness or weakness, severe injuries, or other life-threatening conditions that require immediate medical intervention.