Diving into the intricacies of Emergency Room Care Process, this introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the subject matter. From patient flow to triage and treatment options, get ready to uncover the essentials of emergency care.
As we delve deeper into the emergency care process, we’ll unravel the critical steps involved in providing prompt and effective care to those in need.
Overview of Emergency Room Care Process
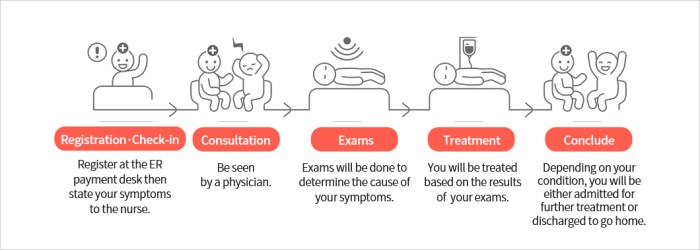
When a patient arrives at the emergency room, the typical flow of their journey involves several key steps to ensure timely and effective care. The process begins with triage, where the severity of the patient’s condition is assessed to prioritize care based on medical urgency.
The Patient’s Journey in the Emergency Room
Upon arrival, the patient is first evaluated by a triage nurse who determines the level of urgency of their condition. This initial assessment helps in directing the patient to the appropriate area of the emergency room for further evaluation and treatment.
- The patient may then undergo diagnostic tests such as blood work, imaging studies, or other procedures to help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis.
- Once a diagnosis is made, the patient will receive the necessary treatment, which may include medications, procedures, or surgery, depending on the severity of their condition.
- Throughout their stay in the emergency room, the patient’s condition is closely monitored, and adjustments to their treatment plan are made as needed to ensure the best possible outcome.
The Importance of Triage in Emergency Care
Triage plays a crucial role in the emergency care process by quickly identifying patients who require immediate attention due to life-threatening conditions. This helps in allocating resources efficiently and providing timely care to those in critical need.
Triage in the Emergency Room
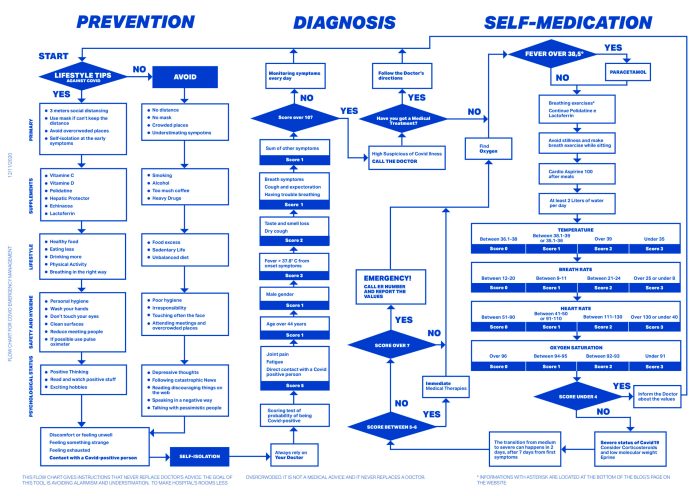
Triage is the process of determining the priority of patients’ treatments based on the severity of their condition. It plays a crucial role in ensuring that patients receive timely and appropriate care in the emergency room.
Different Levels of Triage
- Immediate: Patients with life-threatening conditions that require immediate attention fall under this category.
- Emergent: Patients with serious conditions that need to be addressed promptly but are not immediately life-threatening.
- Urgent: Patients with non-life-threatening conditions that still require medical attention within a reasonable timeframe.
- Non-urgent: Patients with minor injuries or illnesses that can wait for a longer period before receiving treatment.
Triage helps in managing limited resources effectively by ensuring that patients with the most critical conditions are treated first, thus maximizing the use of available medical resources.
Medical Assessment and Diagnosis
Upon a patient’s arrival in the Emergency Room (ER), the medical assessment process begins. This involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s symptoms, medical history, vital signs, and physical examination to determine the severity of the condition and prioritize care.Quick and accurate diagnosis is crucial in the emergency care setting to ensure timely treatment and appropriate intervention. Delays in diagnosis can lead to complications or worsen the patient’s condition, highlighting the importance of efficient assessment and diagnosis in the ER.
Common Diagnostic Tests in the ER
- 1. Blood Tests: Blood samples are often taken to assess various parameters such as complete blood count, electrolyte levels, liver function, and cardiac enzymes.
- 2. Imaging Studies: X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasound are commonly used to visualize internal structures and identify injuries or abnormalities.
- 3. Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test measures the electrical activity of the heart and helps in diagnosing heart conditions such as heart attacks or arrhythmias.
- 4. Urinalysis: Analysis of urine samples can provide valuable information about kidney function, urinary tract infections, and other conditions.
- 5. Rapid Diagnostic Tests: These tests are used to quickly diagnose conditions such as influenza, strep throat, or urinary tract infections.
Treatment and Intervention
When a patient receives treatment in the emergency room, it is crucial to address their medical needs promptly and effectively. This involves a range of treatment options, the expertise of healthcare professionals, and the use of emergency medications and procedures in critical situations.
Role of Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and specialists play a vital role in providing treatment to patients in the emergency room. Doctors are responsible for diagnosing medical conditions, prescribing medications, and overseeing the overall treatment plan. Nurses assist in administering medications, monitoring vital signs, and ensuring patient comfort. Specialists, such as surgeons or cardiologists, may be called upon to provide specialized care depending on the patient’s condition.
Treatment Options
- Medications: Emergency room physicians may prescribe medications to manage pain, reduce inflammation, control infection, or stabilize vital signs.
- Procedures: In critical situations, emergency room staff may need to perform life-saving procedures such as intubation, chest tube insertion, or CPR.
- Surgeries: If a patient requires immediate surgical intervention, emergency room physicians may consult with surgeons to perform procedures such as appendectomies or wound repair.
Emergency Medications and Procedures
- Epinephrine: Used to treat severe allergic reactions (anaphylaxis) by opening airways and increasing blood pressure.
- Defibrillation: Administered to patients experiencing cardiac arrest to restore normal heart rhythm.
- Thrombolytics: Given to patients suffering from a heart attack to dissolve blood clots and restore blood flow to the heart.
Follow-up Care and Discharge

After receiving treatment and intervention in the emergency room, patients are provided with post-treatment care to ensure their well-being before discharge. This follow-up care is crucial in promoting recovery and preventing any complications that may arise after leaving the hospital.
Post-Treatment Care
- Patients are monitored closely by medical staff to assess their response to treatment and ensure that their condition remains stable.
- Medications are prescribed and detailed instructions are given on how to take them correctly, including any potential side effects to watch out for.
- Follow-up appointments are scheduled with primary care physicians or specialists to continue the treatment plan and monitor progress.
Discharge Process and Importance of Clear Instructions
- Before discharge, patients are provided with clear instructions on how to care for themselves at home, including wound care, medication management, and signs to watch for that may indicate a need for medical attention.
- It is crucial for patients to understand these instructions fully to ensure a smooth recovery and reduce the risk of complications that may require further emergency care.
- Clear communication between healthcare providers and patients is essential to ensure that the patient knows what steps to take after leaving the hospital.
Role of Patient Education
- Patient education plays a vital role in preventing future emergencies by empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
- By educating patients on healthy lifestyle choices, medication management, and warning signs of potential health issues, healthcare providers can help individuals take proactive measures to prevent emergencies.
- Engaging patients in their own care through education and guidance can lead to better health outcomes and a reduced likelihood of needing emergency room care in the future.
Importance of Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Emergency Care
Effective interdisciplinary collaboration plays a crucial role in providing quality emergency care to patients. When healthcare professionals from different departments work together seamlessly in the emergency room, it leads to improved patient outcomes and overall efficiency in the care process.
Enhanced Patient Outcomes through Teamwork
In the emergency room setting, teamwork among healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, technicians, and support staff is essential for delivering timely and effective care. For example, when a patient comes in with a complex medical condition requiring immediate intervention, collaboration between the emergency medicine team, surgical team, and radiology team ensures a swift and accurate diagnosis, followed by prompt treatment.
Effective Communication for Coordinated Care
One of the key benefits of interdisciplinary collaboration in emergency care is the enhanced communication between different departments. Clear and concise communication among healthcare professionals ensures that critical information is shared promptly, leading to coordinated care delivery. For instance, when a patient’s condition changes rapidly, effective communication between the nursing staff and the attending physician helps in adjusting the treatment plan promptly.
Successful Interdisciplinary Collaborations in Emergency Care
Numerous successful examples of interdisciplinary collaborations in emergency care exist, showcasing the positive impact of teamwork on patient outcomes. One such example is the rapid response teams in hospitals, where professionals from various departments come together to provide immediate care to patients experiencing medical emergencies. These teams demonstrate how effective collaboration and communication can save lives in critical situations.
Challenges and Innovations in Emergency Care
Emergency care providers face several challenges in delivering timely and effective care to patients in the emergency room. These challenges include overcrowding, long wait times, resource constraints, and the need to prioritize patients based on the severity of their condition.
Common Challenges in Emergency Care
- Overcrowding: Emergency departments often experience overcrowding, leading to delays in care and increased stress for both patients and staff.
- Resource Constraints: Limited resources such as medical equipment, staff, and hospital beds can impact the quality of care provided in the emergency room.
- Wait Times: Long wait times for patients to see a healthcare provider can result in decreased patient satisfaction and poorer health outcomes.
- Triage Decisions: Healthcare providers must make quick decisions to prioritize patients based on the severity of their condition, leading to ethical dilemmas and challenging situations.
Innovations in Emergency Care
- Telemedicine: The use of telemedicine technologies allows remote consultations and assessments, reducing the burden on emergency departments and providing faster access to care.
- Electronic Health Records: Electronic health records streamline information sharing between healthcare providers, improving coordination of care and reducing errors in diagnosis and treatment.
- Point-of-Care Testing: Rapid diagnostic tests conducted at the bedside enable faster decision-making and treatment initiation, improving patient outcomes.
- Simulation Training: Simulation-based training programs help healthcare providers practice emergency scenarios and improve their skills in a controlled environment.
Evolution of Emergency Care Processes
- Collaborative Care Models: Interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals has become increasingly important in emergency care to ensure comprehensive and coordinated patient management.
- Quality Improvement Initiatives: Healthcare organizations are implementing quality improvement initiatives to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of emergency care delivery.
- Community Paramedicine Programs: Community paramedicine programs extend the role of paramedics to provide preventive care and follow-up services, reducing unnecessary emergency room visits.
- Mobile Integrated Healthcare: Mobile integrated healthcare programs deliver care to patients in their homes or communities, improving access to care and reducing hospital admissions.
In conclusion, the Emergency Room Care Process is a multifaceted system that relies on seamless coordination, rapid decision-making, and expert medical interventions to ensure the best outcomes for patients in critical situations.
Quick FAQs
What role does triage play in the Emergency Room Care Process?
Triage is crucial in prioritizing patient care based on the severity of their condition, ensuring that those in critical need receive immediate attention.
How do healthcare professionals collaborate in emergency care?
Healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, and specialists work together cohesively, utilizing their expertise to provide comprehensive and timely treatment to patients.
What are some common challenges faced in emergency care?
Common challenges include managing limited resources efficiently, dealing with high patient volumes, and ensuring rapid decision-making under pressure.