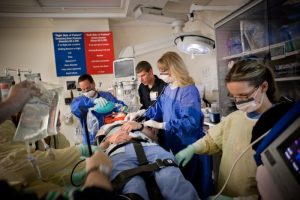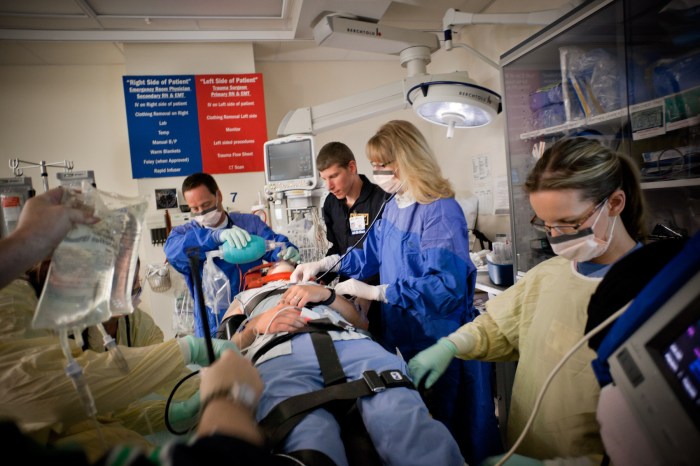
With Emergency Care for Trauma Patients at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling filled with unexpected twists and insights.
When faced with traumatic situations, the swift and effective actions taken in emergency care can be the difference between life and death. Understanding the critical components of providing immediate support is essential in ensuring the best outcomes for trauma patients.
Emergency Care
Emergency care for trauma patients plays a crucial role in ensuring timely and effective treatment to prevent further complications and save lives.
Key Components of Emergency Care Protocols
- Immediate assessment of the patient’s condition upon arrival
- Stabilization of vital signs such as airway, breathing, and circulation
- Rapid diagnostic tests and imaging to identify injuries
- Pain management and controlling bleeding
- Preparation for surgery or other interventions as needed
Role of Triage in Determining Priority
Triage is essential in determining the priority of care for trauma patients based on the severity of their injuries. It helps allocate resources efficiently and ensure that those in critical condition receive immediate attention.
Initial Assessment Steps
- Evaluate the patient’s level of consciousness and airway patency
- Assess breathing and circulation, checking for any signs of respiratory distress or shock
- Examine the patient for visible injuries and assess pain levels
- Gather information on the mechanism of injury and any pre-existing medical conditions
Trauma Assessment
In emergency care, trauma assessment plays a crucial role in ensuring timely and appropriate treatment for patients who have experienced significant injuries. It involves a systematic evaluation to identify the extent of trauma and prioritize interventions based on the severity of injuries.
Primary Goals of Trauma Assessment
- Identifying life-threatening injuries
- Evaluating the mechanism of injury
- Assessing the patient’s physiological status
- Establishing priorities for treatment
Comparison of Assessment Techniques
- Primary survey: Rapid assessment to identify and manage life-threatening conditions
- Secondary survey: Comprehensive head-to-toe assessment to detect all injuries
- Tertiary survey: Ongoing reassessment to monitor changes in patient status
Steps in a Thorough Trauma Assessment
- Scene size-up and safety assessment
- Primary survey (ABCDE approach: Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure)
- History taking and secondary survey
- Adjuncts to assessment (imaging, laboratory tests)
- Reassessment and monitoring
Significance of Systematic Approach
A systematic approach to trauma assessment ensures that no critical injuries are missed and that interventions are prioritized effectively based on the patient’s condition. It helps in providing timely and appropriate care, potentially saving lives in critical situations.
Immediate Interventions
In emergency care for trauma patients, immediate interventions play a crucial role in stabilizing the patient’s condition and preventing further complications. These interventions are aimed at addressing life-threatening issues promptly to increase the patient’s chances of survival.
Airway Management in Traumatic Injuries
Airway management is a critical aspect of emergency care for trauma patients, especially in cases of severe injuries that may compromise the airway. The procedures for airway management include:
- Assessment of airway patency
- Opening the airway using maneuvers like the jaw-thrust or chin-lift
- Insertion of an oral or nasal airway
- Intubation in cases of severe airway compromise
- Continuous monitoring of the airway to ensure adequate oxygenation
Controlling Bleeding in Trauma Patients
Controlling bleeding is crucial in trauma patients to prevent hypovolemic shock and further deterioration. The importance of controlling bleeding includes:
- Direct pressure on the wound to stop external bleeding
- Application of tourniquets in cases of severe bleeding from extremities
- Administration of intravenous fluids and blood products to maintain adequate circulation
- Identification and management of internal bleeding through diagnostic tests and procedures
Principles of Immobilization and Stabilization
Immobilization and stabilization are essential in managing trauma patients to prevent additional injuries and complications. The principles include:
- Assessment of the spine for potential injuries and spinal precautions
- Immobilization of the cervical spine with a cervical collar or sandbags
- Use of backboards and straps for full-body immobilization during transport
- Stabilization of fractures with splints or traction devices
- Continuous monitoring of the patient’s condition for changes or deterioration
Diagnostic Procedures

In emergency care for trauma patients, diagnostic procedures play a crucial role in assessing the extent of injuries and determining the course of treatment.
Imaging Techniques
- X-rays: X-rays are commonly used to visualize bone fractures and detect any dislocations or foreign objects within the body.
- CT scans: CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of internal organs and tissues, helping identify internal bleeding or organ damage.
- Ultrasounds: Ultrasounds are useful in evaluating soft tissue injuries, such as assessing for fluid accumulation or organ abnormalities.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, including blood tests and urine analysis, are essential in evaluating trauma patients by providing valuable information about the patient’s overall health status, blood loss, and organ function.
Role in Treatment Decision-making
Diagnostic procedures aid healthcare providers in making informed decisions regarding the appropriate interventions and treatment strategies for trauma patients. By accurately identifying the injuries and internal complications, healthcare teams can prioritize and deliver timely care to improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the timely and precise interventions discussed in emergency care for trauma patients are crucial in saving lives and promoting recovery. By following established protocols and procedures, healthcare professionals can make a significant impact in the face of adversity.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key components of emergency care protocols for trauma patients?
The key components include rapid assessment, triage to determine priority, immediate interventions to stabilize the patient, and diagnostic procedures for further evaluation.
How important is controlling bleeding in trauma patients?
Controlling bleeding is vital as uncontrolled bleeding can lead to shock and further complications. Proper techniques and tools are employed to manage bleeding effectively.
What role do imaging techniques like X-rays play in diagnosing traumatic injuries?
Imaging techniques such as X-rays help in identifying fractures, foreign objects, and other internal injuries that may not be visible externally, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.